Boreal Owl
Aegolius funereus

Characteristics:
About 10” long, the Boreal Owl has a chocolate brown back with large white spots and white underparts streaked with brown. Its off-white facial disk with a distinct black border, short tail, yellow bill, and white forehead spotting are distinctive field markings.
Hunting Techniques and Prey:
These small, nocturnal owls have good eyesight, but rely more on keen hearing. Their asymmetrical ear openings (the greatest asymmetry of any owl) allow them to pinpoint the location of their small prey. Boreal Owls eat mostly voles but also consume songbirds, shrews and occasionally even bats.
Habitat:
Prefer closed canopy forests of broad-leaved trees or mixed forests with both broad-leaved and spruce trees. They nest in tree cavities usually excavated by woodpeckers and also readily use large nest boxes. They nest from mid-April to early June.

Voice:
Boreal Owl Call (MP3 file 183 kB)
Similar in tone to the saw whet, but delivered in a run of about 12 notes then a pause, then repeated.
The Boreal Owl’s song is a soft trill of constant pitch that lasts for one to two seconds
and is repeated frequently. It sounds similar to the winnowing of a snipe. Twelve high-pitched
notes are given per second. Boreal Owls usually call from mid-February through April though
calls may be heard from January through June.
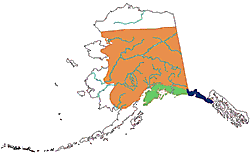
|
|
|
|
Common Uncommon Rare |
 This information is from The Alaska Owlmanac: A guide to the identification, habits, and habitat of ten owl species found in Alaska.
The Alaska Owlmanac (PDF 1,163 kB)
This information is from The Alaska Owlmanac: A guide to the identification, habits, and habitat of ten owl species found in Alaska.
The Alaska Owlmanac (PDF 1,163 kB)
